- +91-9224199672
- drpanchdevg@yahoo.com
- Kalyan West, Maharashtra
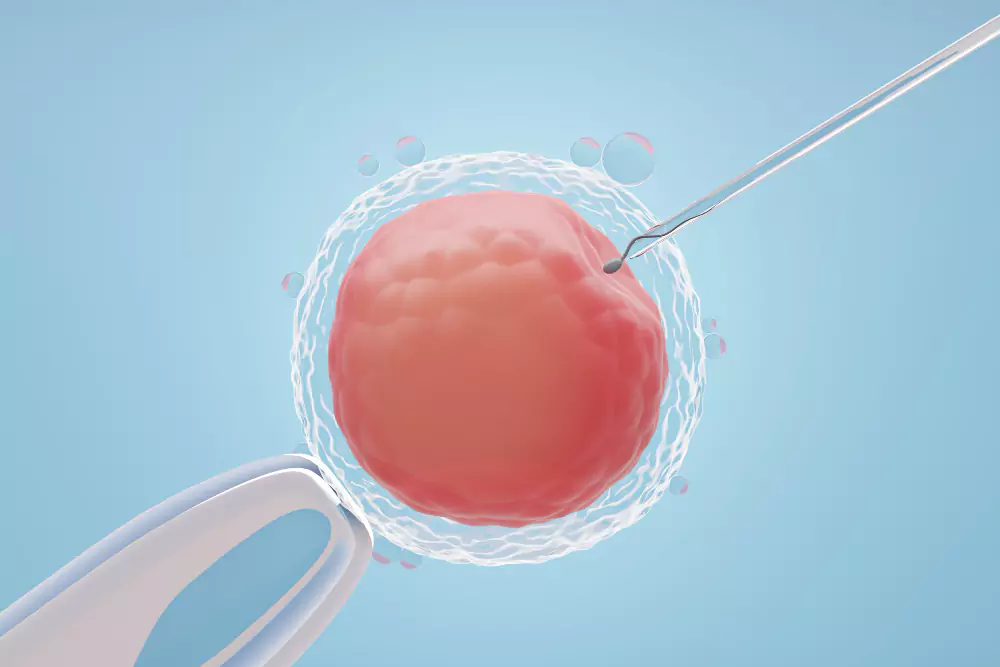
ICSI is an advanced form of IVF where a single sperm is directly injected into the cytoplasm of a mature egg to facilitate fertilization. It’s primarily used when there are significant issues with sperm quality or quantity.
Unlike conventional IVF (where many sperm are left to fertilize the egg naturally in a dish), ICSI manually ensures fertilization with a carefully selected sperm.
ICSI is usually recommended in the following situations:
Low sperm count (oligospermia)
Poor sperm motility (asthenospermia)
Abnormal sperm morphology (teratospermia)
Obstructive azoospermia (sperm retrieved surgically from testicles)
Previous IVF cycle with poor fertilization
Use of frozen sperm or testicular sperm (TESA/PESA)
Antisperm antibodies affecting fertilization
Retrograde ejaculation or spinal cord injuries
Female partner receives hormone injections to produce multiple eggs.
Progress is monitored with blood tests and ultrasounds.
Mature eggs are collected via a minor procedure under sedation.
Eggs are evaluated under a microscope for maturity.
A semen sample is provided or sperm is retrieved surgically (e.g., TESA).
Sperm is washed and processed to select the healthiest, most motile ones.
A single, healthy sperm is immobilized.
Using a microneedle, the sperm is injected directly into the cytoplasm of the egg under a high-powered microscope.
Performed by a highly trained embryologist.
Eggs are checked the next day for signs of fertilization (presence of two pronuclei).
Fertilized eggs are cultured for 3–5 days to develop into embryos or blastocysts.
One or more high-quality embryos are transferred to the uterus.
Remaining embryos can be frozen (cryopreservation).
Blood test (β-hCG) is done 10–14 days after embryo transfer to confirm pregnancy.
Fertilization rate: 70–85% of mature eggs typically fertilize.
Pregnancy rates: Similar to IVF, but ICSI may improve outcomes in male infertility.
Success also depends on egg quality, uterine health, and age of the female partner.
| Feature | IVF | ICSI |
|---|---|---|
| Fertilization | Natural (many sperm compete) | Single sperm injected into egg |
| Indication | General infertility | Male factor infertility |
| Sperm Requirement | Normal semen count | Even very few sperm can be used |
| Use in PGD/PGT | Not always needed | Usually used with genetic testing |
Time-lapse embryo monitoring
Assisted hatching
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT-A / PGT-M)
Embryo glue for implantation support
ICSI is safe and effective, with minimal risk of damage to eggs.
No increased risk of birth defects, as confirmed by long-term studies.
Often used in combination with frozen embryo transfer (FET) for better implantation.

Niraj IVF & Laparoscopy Centre specializes in fertility treatments, including IVF, ICSI, PRP, and laparoscopic surgeries. With cutting-edge technology and personalized care, we help couples overcome infertility challenges and achieve their dream of parenthood.